
The lamellar concept is still sometimes considered to be a useful organizing principle, but more recent data, showing extensive longitudinal connections within the hippocampal system, have required it to be substantially modified. This observation was the basis of his lamellar hypothesis, which proposed that the hippocampus can be thought of as a series of parallel strips, operating in a functionally independent way. The perforant path-to-dentate gyrus-to-CA3-to-CA1 was called the trisynaptic circuit by Per Andersen, who noted that thin slices could be cut out of the hippocampus perpendicular to its long axis, in a way that preserves all of these connections. Subicular neurons send their axons mainly to the EC. Pyramidal cells of CA1 send their axons to the subiculum and deep layers of the EC. Pyramidal cells of CA3 send their axons to CA1. Granule cells of the DG send their axons (called "mossy fibers") to CA3. There is also a distinct pathway from layer 3 of the EC directly to CA1. These axons arise from layer 2 of the EC, and terminate in the dentate gyrus and CA3. Most external input comes from the adjoining entorhinal cortex, via the axons of the so-called perforant path. The major pathways of signal flow through the hippocampus combine to form a loop. Most anatomistsuse the term "hippocampus proper" to refer to the four CA fields, and "hippocampal formation"to refer to the hippocampus proper plus dentate gyrus and subiculum. After this come a pair of ill-defined areas called the presubiculum and parasubiculum, then atransition to the cortex proper (mostly the entorhinal area of the cortex). After CA1 comes an area called the subiculum. The CA areas are all filled with densely packed pyramidal cells similar to those found in the neocortex. Nextcome a series of Cornu Ammonis areas: first CA4 (which underlies the dentate gyrus), then CA3, thena very small zone called CA2, then CA1.
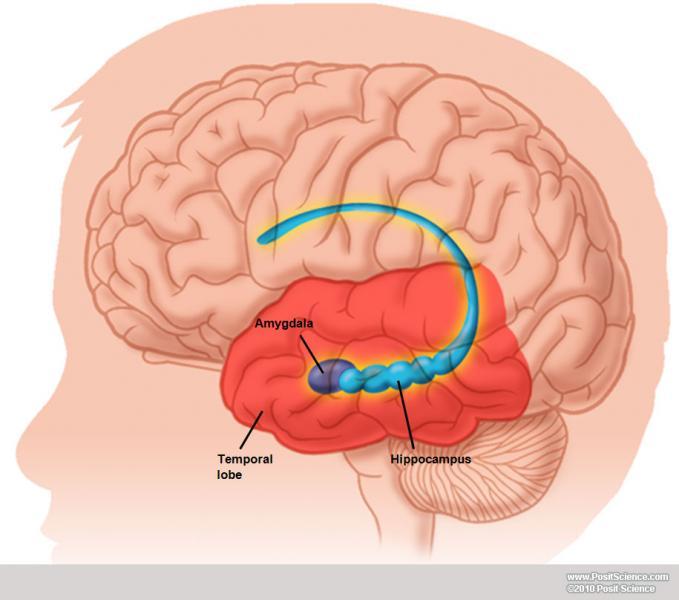

The first of these, the dentate gyrus (DG), is actually a separatestructure, a tightly packed layer of small granule cells wrapped around the end of the hippocampusproper, forming a pointed wedge in some cross-sections, a semicircle in others. Starting at the dentate gyrus and working inward along the S-curve of the hippocampus means traversing aseries of narrow zones. Basic circuit of the hippocampus, shown using a modified drawing by Ramon y Cajal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
